
Introduction
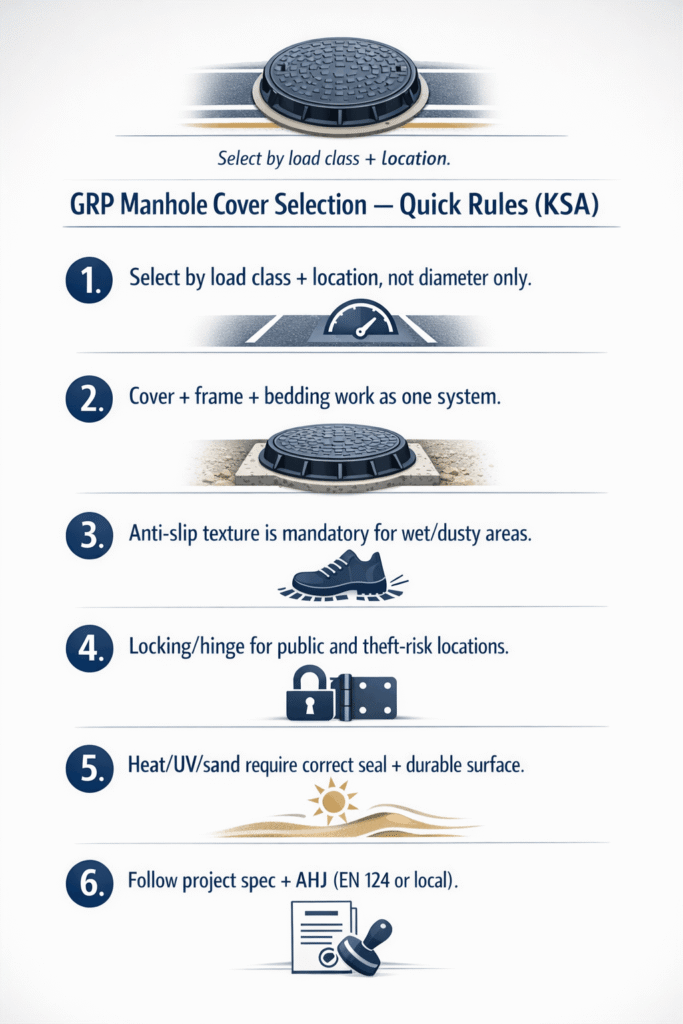
Selecting the right GRP manhole cover in Saudi Arabia is a safety and durability decision, not a cosmetic one. The wrong load class or frame detail can lead to rocking, noise, premature cracking, accidents, or even cover ejection under traffic. Aggressive KSA/GCC conditions—high heat, UV, sand, coastal salinity, and H₂S in sewage—accelerate corrosion and wear, especially for metal covers. This guide explains what a GRP/composite manhole system is, common cover types, EN 124 manhole cover classes and other manhole cover load rating concepts, and where each is used in KSA. You will also get a simple, practical selection checklist and RFQ template to specify the correct GRP manhole cover Saudi Arabia projects need, aligned with project specifications and authority requirements.
Quick Answer
- GRP/composite covers resist corrosion in sewage, industrial, and coastal environments where metal covers suffer from rust and chemical attack.
- Always select by required GRP manhole load class and location (group/area), not by “diameter only.
- The frame type, depth, and concrete bedding are as important as the cover when designing a GRP manhole cover Saudi Arabia installation.
- Anti-slip surface and locking/hinges are critical for public areas, wet zones, and high pedestrian exposure.
- Most rocking/noise and many failures come from poor installation, not just material choice.
- Heat, UV, and wind-blown sand require the right sealing system and a surface texture that stays slip-resistant over time.
- Always follow project specifications and AHJ (authority having jurisdiction) requirements; standards and load classes can differ by municipality.
- For a correct quotation, you must send: location and traffic type, required standard/load class, clear opening, frame depth, sealing/locking needs, surface texture, quantities, and delivery location in KSA.
What Is a GRP/Composite Manhole System?
A GRP/composite manhole system combines a corrosion resistant manhole cover with a matching frame and seating/bedding designed to work as one unit under load. In a typical sewage manhole cover KSA application, the GRP cover sits on the frame, which is set in concrete or asphalt with proper bedding to spread vehicle loads into the surrounding structure. Optional components include gaskets or seals for odor/gas control, locking or bolted systems for security, hinges to prevent removal, and lifting points compatible with safe keys or hooks. Treating the cover alone as the “solution” often leads to failures; the system must match the specified EN 124 manhole cover classes or other project standards, plus local construction practice.
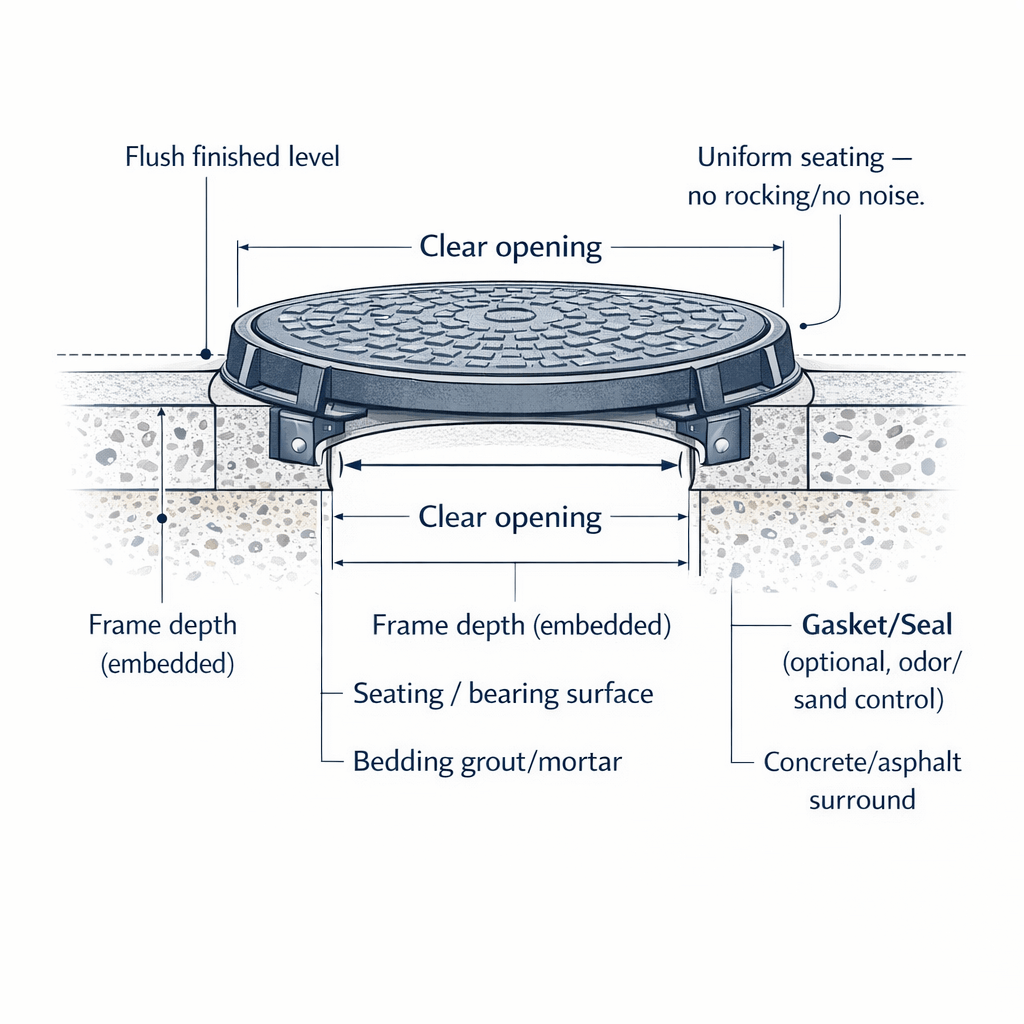
Key terms (for drawings and RFQs)
- Clear opening: Effective internal opening available for access; typically defined by EN 124 or project standard.
- Overall size: Outside dimension of the frame (and cover), critical for matching to existing slabs or new formwork.
- Frame depth: Vertical height of the frame section that will be embedded in concrete or paving.
- Seating: Bearing area where the cover contacts the frame, including any steps or rebates.
- Gasket: Compressible seal used to limit water ingress, odor escape, or gas leakage.
- Lock: Mechanical or coded device that prevents unauthorized opening, often tested for tamper resistance.
- Anti-slip: Surface texture or coating designed to improve skid resistance, especially when wet or dusty.
Types of GRP Manholes and Covers
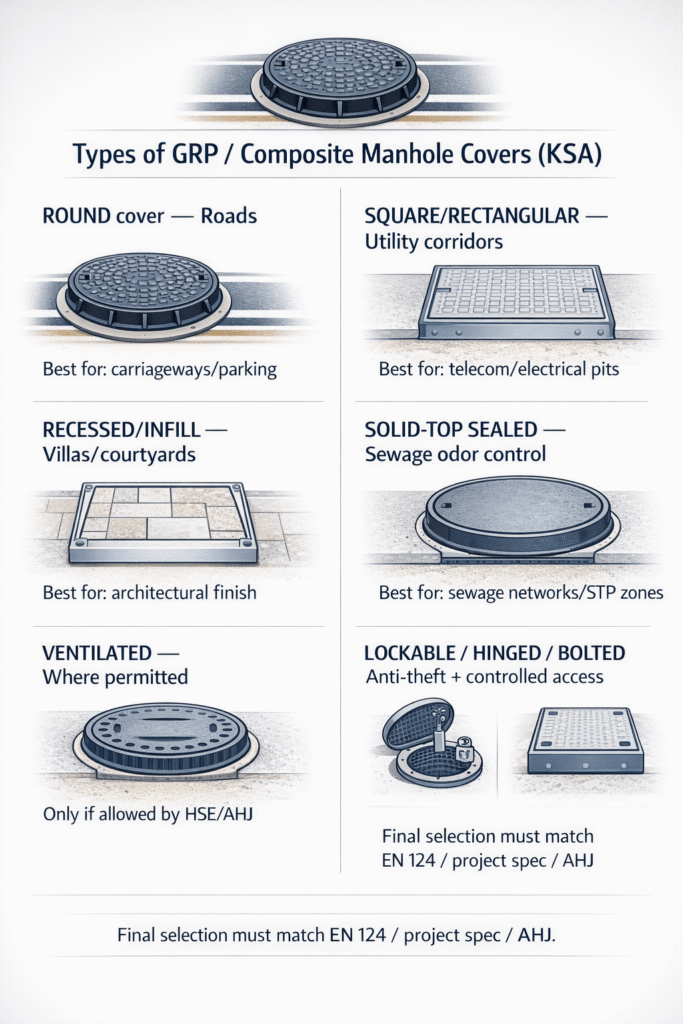
Round covers (common in roads)
Round GRP manhole cover Saudi Arabia designs are widely used in roadways because they do not fall through their openings and distribute traffic loads uniformly. They are typically specified for carriageways, shoulders, and parking areas where EN 124 D or higher classes (or equivalent) are required.
Square/rectangular covers (utility corridors)
Square or rectangular composite manhole cover systems are common for utility corridors, valve chambers, and electrical/telecom pits where equipment layout is rectangular. They can offer easier alignment with duct banks and trench walls but require attention to frame seating to control rocking.
Recessed/infill covers (tiles/pavers in villas)
Recessed or infill GRP covers allow tiles, pavers, or concrete topping to be placed in the tray so the finish matches the surrounding surface. In KSA villas and courtyards, these are often used in non-traffic or light-traffic areas where architectural appearance is important and a lighter load class is acceptable per project specs.
Solid top vs ventilated
Solid-top covers are used when odor, gas, or water ingress must be minimized, such as sewage manhole cover KSA networks in residential or commercial streets. Ventilated covers or covers with vent holes may be used for chambers that need passive ventilation, but openings must not compromise safety or allow hazardous gases into pedestrian zones; final design must follow project HSE requirements.
Lockable / hinged / bolted
Lockable and hinged GRP manhole cover Saudi Arabia solutions help prevent unauthorized opening, theft, and accidental dislodging in public areas. Bolted covers or security-code mechanisms are often specified in telecom, high-risk, or critical infrastructure sites to create an anti theft manhole cover system.
Sealed (odor/gas control)
Sealed covers use gaskets and close tolerances between the cover and frame to help limit odor and gas escape from H₂S-rich sewage networks, pumping stations, and STPs. For aggressive environments, sealing materials must be compatible with sewage gases and cleaning chemicals; this should be confirmed against project chemical exposure and AHJ requirements.
Load Classes Explained (How Ratings Work)
Load rating defines how much static test load a manhole cover and frame can withstand under standardized conditions. EN 124 (and its national adoptions such as BS EN 124) is a widely used standard that groups applications and specifies manhole cover load rating classes (A15 to F900) with defined test loads and installation areas. Under BS EN 124:2015, for example, covers are tested at specified kN loads (such as 125 kN for B125, 250 kN for C250, 400 kN for D400, and 600 kN for E600) to ensure suitability for different traffic areas. Many Gulf authorities refer to EN 124 manhole cover classes while also issuing their own municipal or highway specifications, so KSA projects often follow a mix of EN 124, AASHTO, and local requirements. Always confirm with project specifications and the AHJ which standard, group, and load class apply.
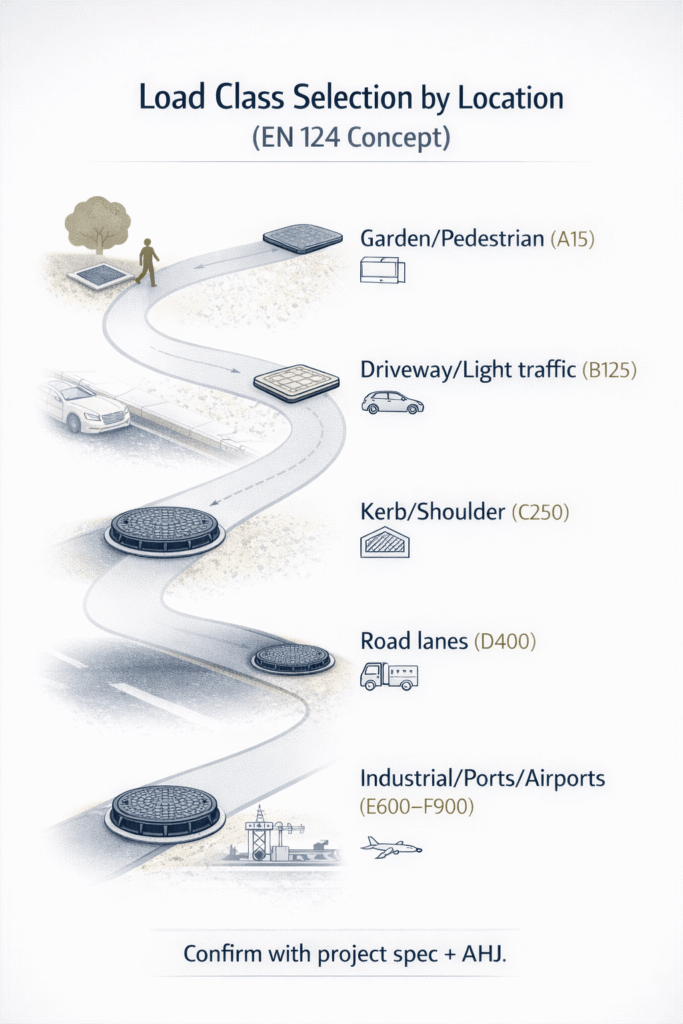
Location is the starting point:
- Gardens and pedestrian zones typically use lower classes (e.g., A or B groups under EN 124 or similar).
- Road lanes and heavy industrial areas in KSA commonly require D or higher, sometimes E or F for extreme loads like ports and airports.
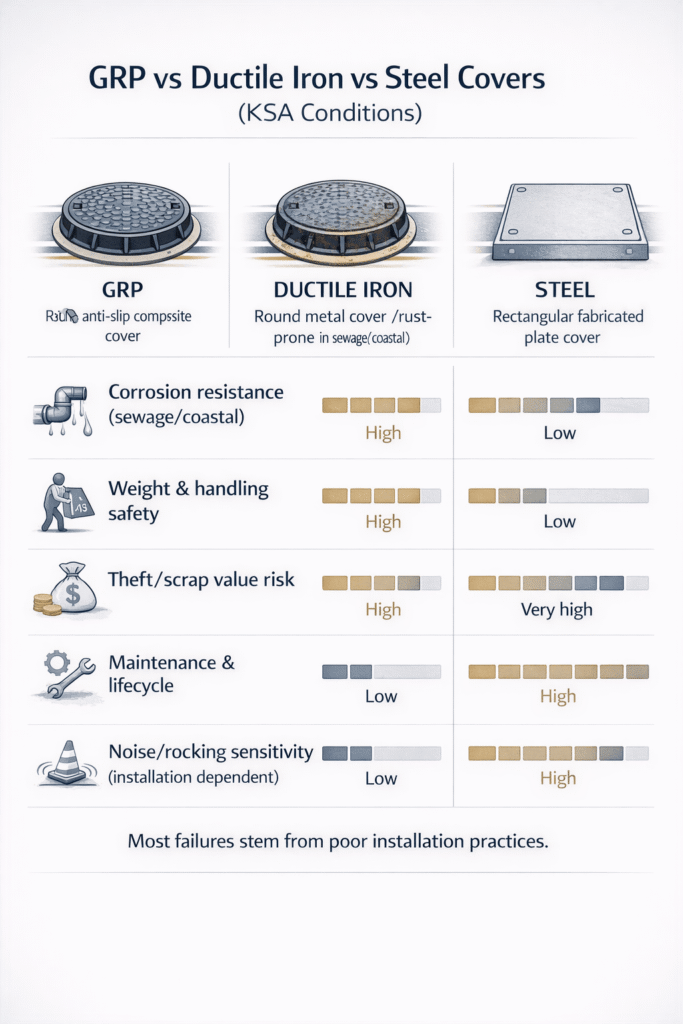
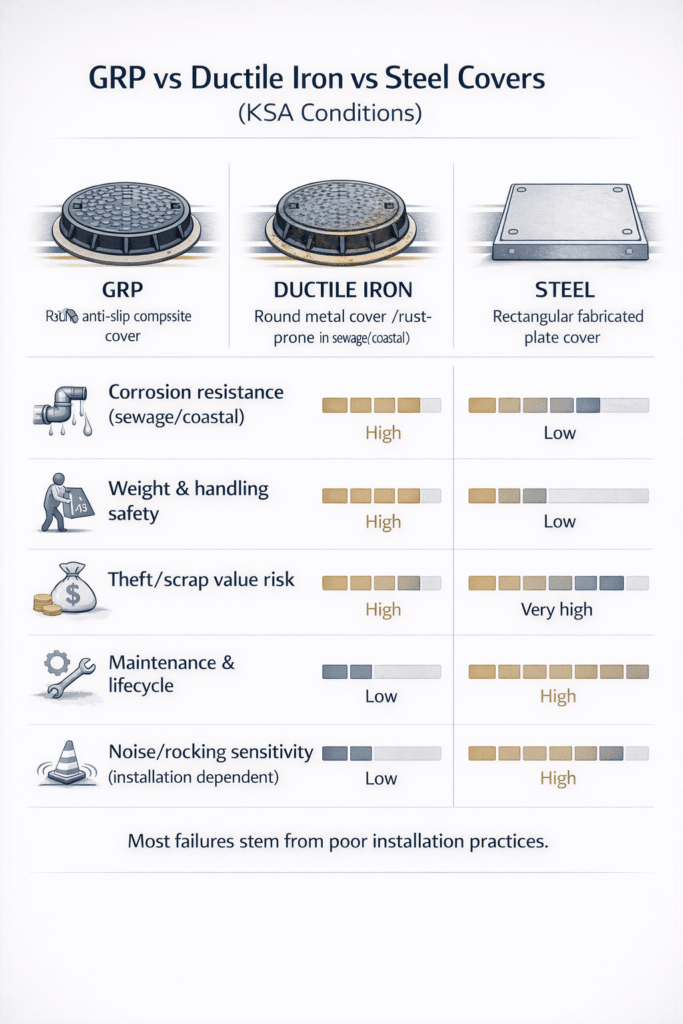
GRP vs Ductile Iron vs Steel Covers (KSA Reality)
In Saudi Arabia, corrosion, temperature cycling, and sand ingress give GRP/composite covers different lifecycle behavior compared with ductile iron or fabricated steel. Properly designed composite manhole cover products offer low scrap value, good corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation, while metals remain strong and stiff but vulnerable to rust and theft. The right choice depends on load class, environment (sewage, coastal, industrial), budget, and maintenance capability, not material alone.
Applications in Saudi Arabia (Where Each Type Fits)
Municipal roads and highways
For municipal roads and highways, GRP manhole cover Saudi Arabia specifications often call for high EN 124 classes (e.g., D or higher) or equivalent, with robust frames and deep seating. Preferred features include anti-slip surfaces, secure locking or hinged systems, proper sealing against sand ingress, and frames designed for asphalt or concrete pavements.
Industrial plants and warehouses
Industrial plants and warehouses may have forklift, trailer, or heavy truck loads plus exposure to oils, chemicals, or cleaning agents. Here, designers typically look for corrosion resistant manhole cover systems with chemical-resistant resin, correct load class, anti-slip surfaces, and clear locking procedures for permit-to-work regimes.
Residential/villas (courtyards, driveways, gardens)
In villas and residential compounds, recessed/infill GRP covers blend with paving, while round or square solid-top covers are used in driveways and gardens. Load class is selected for car/light vehicle traffic where needed, and anti-slip plus child-resistant locking is often desirable around play areas and swimming pools.
STP/WWTP sites and sewage networks
STPs, WWTPs, and trunk sewers experience continuous H₂S and moisture, plus occasional chemical cleaning. GRP/composite sewage manhole cover KSA designs are attractive due to their resistance to sewage gas corrosion and reduced maintenance compared with bare ductile iron, but sealing, ventilation strategy, and gas monitoring must follow process/HSE specifications.
Coastal regions
Coastal KSA locations see chloride-laden air, salt spray, and often high groundwater salinity, which accelerate metal corrosion. Corrosion resistant manhole cover systems in GRP are well suited here, provided frames and reinforcement details are selected for the load rating and anchorage conditions.
Remote sites with limited maintenance
In remote sites such as pipelines, telecom routes, or desert facilities, access for maintenance is infrequent and theft risk may be higher. Lightweight GRP covers simplify manual handling and reduce need for lifting equipment, while anti theft manhole cover features (locking, hinges, coded keys) help maintain system integrity between inspections.
Installation Best Practices (Prevents Failures)
Step-by-step checklist
- Confirm load class & clear opening against project drawings and the specified standard (EN 124 or alternative).
- Prepare a level, sound base for the frame, with adequate concrete thickness and reinforcement as per civil design.
- Use the correct bedding material (mortar or grout type, thickness) and compaction around the frame to avoid voids.
- Align the frame so the finished level is flush with pavement (or per design) to avoid trip edges and impact loads.
- Install gasket or seal (if specified), clean seating surfaces, and ensure uniform contact around the perimeter.
- Apply specified torque for bolts or locking mechanisms in a cross pattern, following manufacturer/standard guidelines.
- Perform site acceptance checks: rock test (check for movement under load), noise check under wheel pass, and surface finish/anti-slip verification.
What inspectors look for
- Correct standard marking and load class on the cover/frame where required.
- Frame level and alignment relative to road or pavement surface.
- Absence of visible rocking or rattling when trafficked.
- Undamaged sealing surfaces and properly seated gaskets (if specified).
- Clean anti-slip surface, free from laitance, excess grout, or heavy polishing.
Common Failure Modes (And How to Avoid Them)
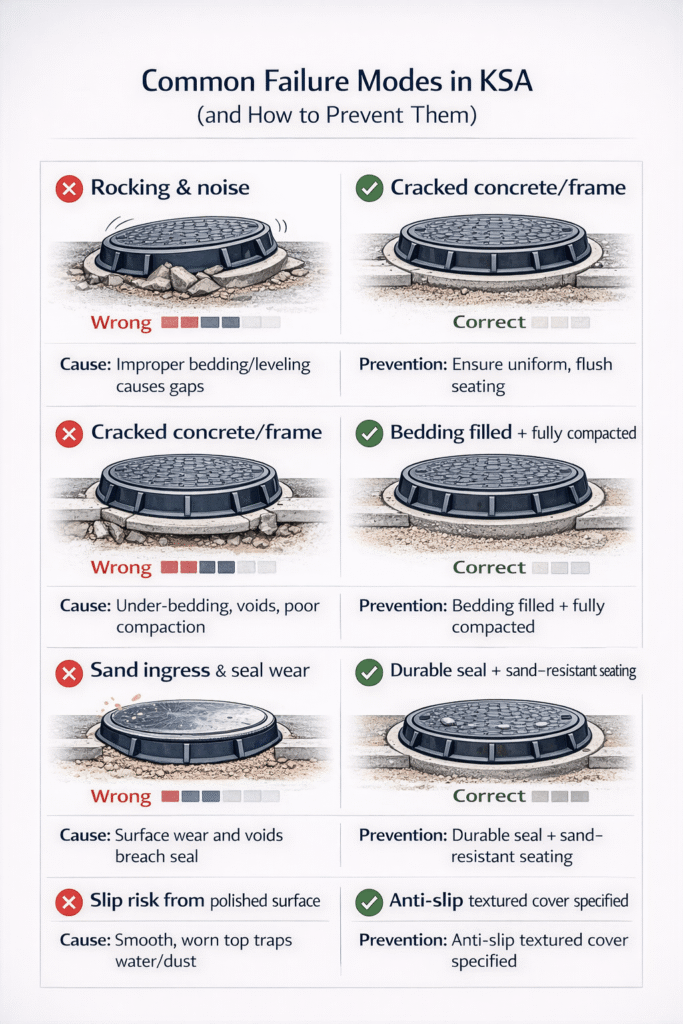
Rocking and noise usually result from inadequate bedding, poor compaction around the frame, or mismatched seating surfaces. Cracking of frames or surrounding concrete can occur when the installed cover/frame load class is lower than the actual traffic or when voids exist beneath the frame. Surface polishing and slip risk may develop in high-traffic pedestrian areas if anti-slip texture is insufficient or becomes clogged with fines and not cleaned. Sand ingress and seal wear are common in KSA due to wind-blown dust; incorrect or poorly maintained seals allow abrasive particles to accelerate wear and make opening/closing difficult. Using a lower GRP manhole load class than required in traffic lanes, or omitting locking where theft is a risk, can lead to dangerous conditions and non-compliance with AHJ requirements.i
Selection Checklist (What to Send in an RFQ)
- Location: road lane / shoulder / parking / footpath / courtyard / garden / plant area.
- Traffic type: pedestrians / light vehicles / trucks / forklifts / special loads (ports, airports, etc.).
- Required standard / load class: EN 124 group/class, AASHTO, or client/AHJ standard (attach spec or drawing where possible).
- Clear opening size: internal diameter or width × length as specified.
- Overall frame size and tolerance limits (to fit existing chambers or new construction).
- Frame type and depth: for concrete/asphalt, with any special edge details.
- Sealing requirement: odor control / gas-tight / water ingress limit (including expected H₂S or chemical exposure).
- Locking/hinge requirement: lockable, hinged, bolted, or free-lift, with any keying or security-code preferences.
- Surface: anti-slip texture level, pattern preference if specified.
- Color requirement (if any) for identification or architectural reasons.
- Quantity, phasing, and delivery locations within KSA (city, site type, delivery constraints).
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Choosing by “diameter only” and ignoring EN 124 manhole cover classes or equivalent load group.
- Under-rating load class in traffic areas or truck access routes.
- Ignoring frame depth and bedding quality, leading to rocking frames and broken concrete.
- Installing covers above or below pavement level, causing impact loads or trip hazards.
- Omitting anti-slip requirements in wet or sloped areas such as STPs or near wash-down zones.
- Skipping locking in public or remote areas where an anti theft manhole cover is needed.
- Poor compaction of backfill around frames, creating voids and differential settlement.
- Using the wrong seal material or no seal where gas/odor control is specified.
- No defined lifting key or safe lifting procedure for composite manhole cover handling.
- Not considering coastal sewage corrosion and H₂S when choosing between GRP and ductile iron.
- No inspection after installation to verify load testing, markings, and fit.
- No maintenance/cleaning plan to remove sand and debris from seating and anti-slip surfaces.
FAQs
Q1: What is a GRP manhole cover?
A GRP manhole cover is a composite manhole cover made from glass-fibre-reinforced polymer, offering high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation compared with metal covers.
Q2: How do I choose the correct load class?
Start from the location and traffic category (pedestrian, driveway, road, industrial) and then match it to the required EN 124 group/class or equivalent in the project specification. Always confirm with AHJ/project specs, as some KSA municipalities publish their own tables of minimum manhole cover load rating by road type.
Q3: Are GRP manhole covers suitable for roads?
Yes, composite manhole cover designs can be engineered and tested for high load classes (e.g., up to D and E groups under EN 124 or similar) and are used on roads in many regions when correctly installed. The frame design, bedding, and adherence to installation guidance are essential to achieve long-term performance in roadways.
Q4: GRP vs ductile iron manhole cover: which is better in KSA?
GRP offers superior resistance to sewage and coastal corrosion, lower weight, and lower theft value, while ductile iron is very stiff and long-proven in heavy traffic areas. In KSA, GRP often has lifecycle advantages where corrosion and theft are concerns, but the “better” option is the one that meets the required load class, standard, and environmental conditions in the project specification.
Q5: What is EN 124 and why does it matter?
EN 124 (and BS EN 124) is a European standard for gully tops and manhole tops for vehicular and pedestrian areas, defining groups, load classes, and test methods for covers and frames. It matters because many clients and authorities use its EN 124 manhole cover classes as the basis for specifying where each cover type can be installed safely.
Q6: Do I need a lockable manhole cover?
You need a lockable or bolted cover wherever unauthorized access, theft, or accidental opening presents safety or operational risks, such as public walkways, telecom chambers, or remote critical infrastructure. Project HSE plans and AHJ guidelines should define where an anti theft manhole cover system is mandatory.
Q7: What causes manhole covers to rock and make noise?
Rocking and noise usually come from uneven seating, poor bedding, settlement around the frame, or wear from debris between the cover and frame. Selecting the right frame depth and following best-practice installation and maintenance greatly reduces these issues.
Q8: Are composite manhole covers anti-theft?
Composite covers typically have low scrap value compared with metal covers and can incorporate locking or coded mechanisms, making them less attractive to thieves. This anti theft manhole cover characteristic is a key reason GRP manhole cover Saudi Arabia usage is increasing in public networks.
Conclusion
Selecting the right GRP manhole cover Saudi Arabia solution requires aligning type, load class, and material with actual site conditions, from road traffic to sewage gas and coastal salinity. By treating the cover, frame, and bedding as a complete system and following recognized standards plus AHJ requirements, owners can reduce failures, noise complaints, and corrosion-related replacements. If you would like project-specific support, you can Request a Quote with your RFQ checklist or Talk to our engineers to review standards, exposure, and load classes for your KSA or GCC site. Final selection must always match project specifications and AHJ requirements.
Table 1 – Types of GRP Covers and Common Pitfalls
| Type | Best location | Key benefit | Common mistake |
|---|---|---|---|
| Round cover | Municipal roads, shoulders, and parking areas with vehicular traffic. | Uniform load distribution, no orientation issues, widely recognized for road use. | Selecting by diameter without verifying required GRP manhole load class and road group. |
| Square/rectangular cover | Utility corridors, valve chambers, electrical/telecom pits. | Matches rectangular chambers and duct banks, efficient access to equipment. | Inadequate seating area at corners and poor frame alignment leading to rocking. |
| Recessed/infill cover | Villas, courtyards, plazas, light-traffic decorative areas. | Allows tiles or pavers on top for seamless architectural finish. | Using in heavy-traffic lanes without suitable load class or structural detailing. |
| Solid-top cover | Sewage and utility chambers where odor and water ingress must be controlled. | Helps control odor/gas escape and limits water/sand ingress when combined with seals. | Assuming solid top alone is gas-tight without specifying gasket and seating design. |
| Ventilated cover | Chambers needing passive ventilation, such as some telecom or drainage structures. | Allows airflow to reduce heat or gas buildup where permitted by HSE rules. | Using ventilation where gas accumulation can be hazardous at surface level. |
| Lockable/hinged/bolted cover | Public areas, remote infrastructure, telecom pits, industrial plants. | Anti theft manhole cover function, improved safety and controlled access. | Installing without clear key control/maintenance procedures, leading to forced opening and damage. |
| Sealed (odor/gas control) cover | Sewage manholes, STPs, WWTPs, pumping stations, H₂S-prone networks. | Enhanced odor/gas control when combined with suitable gaskets and frame design. | Incorrect gasket material selection for sewage/chemical exposure, causing early seal failure. |
Table 2 – Example Load Classes and Typical Areas (based on EN 124 concepts – confirm with project specs/AHJ)
Table 3 – GRP vs Ductile Iron vs Steel Covers (KSA Conditions)
| Feature | GRP/Composite | Ductile iron | Steel (fabricated) | KSA notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion resistance (sewage/coastal) | Non-metallic, very good resistance to sewage gases and coastal salinity; no rusting. | Good mechanical strength but subject to rust in sewage and coastal environments without coatings. | Can be protected initially by coatings, but prone to corrosion damage if coating is breached. | In coastal sewage networks and STPs, GRP reduces corrosion-driven maintenance versus bare metals. |
| Weight & handling safety | Lightweight, often manageable by fewer workers, reducing manual handling risk. | Heavy; may require lifting equipment and poses higher manual handling risk. | Weight varies but generally heavier than GRP; may also need equipment for safe handling. | Lower weight is attractive where frequent opening is required or lifting equipment is limited. |
| Theft value / scrap risk | Low scrap value; composite material is not attractive to metal thieves. | High scrap value; theft of iron covers is widely documented and can cause accidents. | Also has scrap value; cut-and-remove theft is possible in remote areas. | Anti theft manhole cover strategies often favor GRP in theft-prone KSA locations. |
| Electrical insulation / spark risk | Electrically insulating, non-sparking surface. | Conductive; can spark if impacted by metal tools. | Conductive; similar spark considerations as ductile iron. | GRP is advantageous near electrical/telecom installations or flammable atmospheres where insulation is desired. |
| Noise/rocking risk (installation-related) | Low inherent noise if seating is good; rocking mainly a function of frame/bedding quality. | Can rattle and be noisy if seating tolerances or bedding are poor. | Similar to ductile iron; fabricated tolerances affect noise behavior. | For all materials, KSA roads need careful installation to minimize rocking on high-speed traffic routes. |
| Maintenance and lifecycle | Resistant to rust and many chemicals; no repainting, potentially longer service life with proper UV-resistant resin system. | Proven long-term performance but may need repainting, surface treatment, or replacement in corrosive zones. | Maintenance dependent on coating system; unprotected steel is not suitable for sewage/coastal exposure. | GRP can improve lifecycle cost where corrosion and theft drive frequent replacement of metal covers. |